111/TCP/UDP - Pentesting Portmapper
[AD REMOVED]
Basic Information
Portmapper is a service that is utilized for mapping network service ports to RPC (Remote Procedure Call) program numbers. It acts as a critical component in Unix-based systems, facilitating the exchange of information between these systems. The port associated with Portmapper is frequently scanned by attackers as it can reveal valuable information. This information includes the type of Unix Operating System (OS) running and details about the services that are available on the system. Additionally, Portmapper is commonly used in conjunction with NFS (Network File System), NIS (Network Information Service), and other RPC-based services to manage network services effectively.
Default port: 111/TCP/UDP, 32771 in Oracle Solaris
Enumeration
Sometimes it doesn't give you any information, in other occasions you will get something like this:
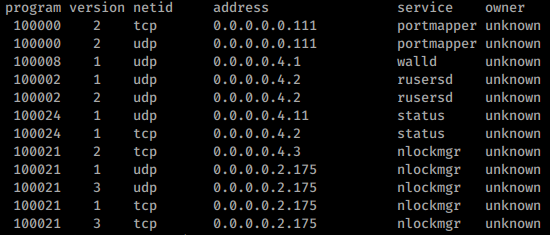
Shodan
port:111 portmap
RPCBind + NFS
If you find the service NFS then probably you will be able to list and download(and maybe upload) files:
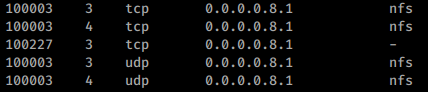
Read 2049 - Pentesting NFS service to learn more about how to test this protocol.
NIS
Exploring NIS vulnerabilities involves a two-step process, starting with the identification of the service ypbind. The cornerstone of this exploration is uncovering the NIS domain name, without which progress is halted.
The exploration journey begins with the installation of necessary packages (apt-get install nis). The subsequent step requires using ypwhich to confirm the NIS server's presence by pinging it with the domain name and server IP, ensuring these elements are anonymized for security.
The final and crucial step involves the ypcat command to extract sensitive data, particularly encrypted user passwords. These hashes, once cracked using tools like John the Ripper, reveal insights into system access and privileges.
# Install NIS tools
apt-get install nis
# Ping the NIS server to confirm its presence
ypwhich -d <domain-name> <server-ip>
# Extract user credentials
ypcat –d <domain-name> –h <server-ip> passwd.byname
NIF files
| Master file | Map(s) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| /etc/hosts | hosts.byname, hosts.byaddr | Contains hostnames and IP details |
| /etc/passwd | passwd.byname, passwd.byuid | NIS user password file |
| /etc/group | group.byname, group.bygid | NIS group file |
| /usr/lib/aliases | mail.aliases | Details mail aliases |
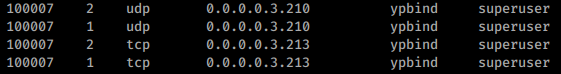
RPC Users
If you find the rusersd service listed like this:

You could enumerate users of the box. To learn how read 1026 - Pentesting Rsusersd.
Bypass Filtered Portmapper port
When conducting a nmap scan and discovering open NFS ports with port 111 being filtered, direct exploitation of these ports is not feasible. However, by simulating a portmapper service locally and creating a tunnel from your machine to the target, exploitation becomes possible using standard tools. This technique allows for bypassing the filtered state of port 111, thus enabling access to NFS services. For detailed guidance on this method, refer to the article available at this link.
Shodan
Portmap
Labs to practice
- Practice these techniques in the Irked HTB machine.
HackTricks Automatic Commands
Protocol_Name: Portmapper #Protocol Abbreviation if there is one.
Port_Number: 43 #Comma separated if there is more than one.
Protocol_Description: PM or RPCBind #Protocol Abbreviation Spelled out
Entry_1:
Name: Notes
Description: Notes for PortMapper
Note: |
Portmapper is a service that is utilized for mapping network service ports to RPC (Remote Procedure Call) program numbers. It acts as a critical component in Unix-based systems, facilitating the exchange of information between these systems. The port associated with Portmapper is frequently scanned by attackers as it can reveal valuable information. This information includes the type of Unix Operating System (OS) running and details about the services that are available on the system. Additionally, Portmapper is commonly used in conjunction with NFS (Network File System), NIS (Network Information Service), and other RPC-based services to manage network services effectively.
https://book.hacktricks.xyz/pentesting/pentesting-rpcbind
Entry_2:
Name: rpc info
Description: May give netstat-type info
Command: whois -h {IP} -p 43 {Domain_Name} && echo {Domain_Name} | nc -vn {IP} 43
Entry_3:
Name: nmap
Description: May give netstat-type info
Command: nmap -sSUC -p 111 {IP}
[AD REMOVED]