unlink
[AD REMOVED]
Code
// From https://github.com/bminor/glibc/blob/master/malloc/malloc.c
/* Take a chunk off a bin list. */
static void
unlink_chunk (mstate av, mchunkptr p)
{
if (chunksize (p) != prev_size (next_chunk (p)))
malloc_printerr ("corrupted size vs. prev_size");
mchunkptr fd = p->fd;
mchunkptr bk = p->bk;
if (__builtin_expect (fd->bk != p || bk->fd != p, 0))
malloc_printerr ("corrupted double-linked list");
fd->bk = bk;
bk->fd = fd;
if (!in_smallbin_range (chunksize_nomask (p)) && p->fd_nextsize != NULL)
{
if (p->fd_nextsize->bk_nextsize != p
|| p->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize != p)
malloc_printerr ("corrupted double-linked list (not small)");
// Added: If the FD is not in the nextsize list
if (fd->fd_nextsize == NULL)
{
if (p->fd_nextsize == p)
fd->fd_nextsize = fd->bk_nextsize = fd;
else
// Link the nexsize list in when removing the new chunk
{
fd->fd_nextsize = p->fd_nextsize;
fd->bk_nextsize = p->bk_nextsize;
p->fd_nextsize->bk_nextsize = fd;
p->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize = fd;
}
}
else
{
p->fd_nextsize->bk_nextsize = p->bk_nextsize;
p->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize = p->fd_nextsize;
}
}
}
Graphical Explanation
Check this great graphical explanation of the unlink process:
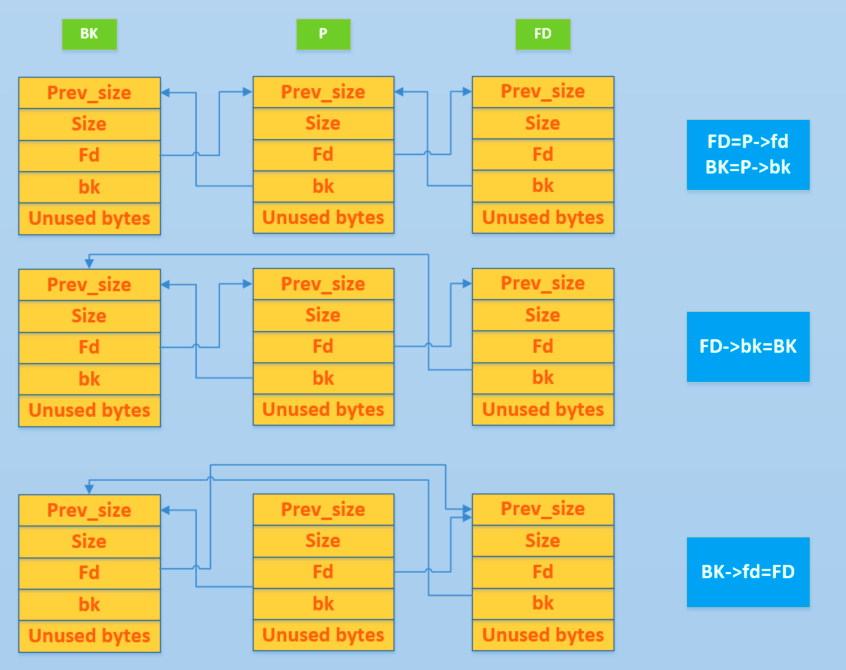
Security Checks
- Check if the indicated size of the chunk is the same as the prev_size indicated in the next chunk
- Check also that
P->fd->bk == PandP->bk->fw == P - If the chunk is not small, check that
P->fd_nextsize->bk_nextsize == PandP->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize == P
Leaks
An unlinked chunk is not cleaning the allocated addreses, so having access to rad it, it's possible to leak some interesting addresses:
Libc Leaks:
- If P is located in the head of the doubly linked list,
bkwill be pointing tomalloc_statein libc - If P is located at the end of the doubly linked list,
fdwill be pointing tomalloc_statein libc - When the doubly linked list contains only one free chunk, P is in the doubly linked list, and both
fdandbkcan leak the address insidemalloc_state.
Heap leaks:
- If P is located in the head of the doubly linked list,
fdwill be pointing to an available chunk in the heap - If P is located at the end of the doubly linked list,
bkwill be pointing to an available chunk in the heap - If P is in the doubly linked list, both
fdandbkwill be pointing to an available chunk in the heap
[AD REMOVED]